No products in the cart.
Data Engineering
Data engineering involves designing, constructing, and maintaining systems and procedures for the effective gathering, storing, processing, and analysis of data is known as data engineering. This allows businesses to gain insightful knowledge and make wise choices.

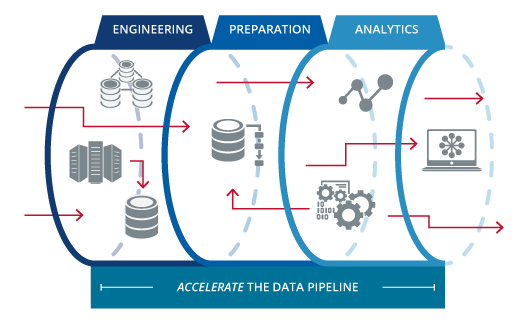
Data Pipeline
Three primary components comprise a data pipeline:
- 1) Data sources
- 2) Data processing (ETL/ELT)
- 3) Data storage
Data sources of the data are those sources. Anything may be used, including file uploads, apps, cloud storage, and the Internet of things.
Data processing is the process of removing unprocessed data from its sources, transforming it, and then loading it into data storage.
This is known as Extract, Transform, Load, or ETL for that reason. Data is extracted from the sources and then organized, cleaned, altered, and validated to make it useable. Put succinctly, data is jumbled. The data is saved after this stage is complete.
Another such procedure is known as Extract, Load, and Transform, or ELT. Data extraction is followed by data storage, and data transformation is done only after that.
Data storage is the location where processed data is stored following processing. It’s often a data lake or warehouse. Business users and other data specialists can then access the data.
Features
Data Pipeline Development
Data Pipeline Development: Creating, constructing, and maintaining data pipelines is one of the core duties of data engineers. These pipelines make sure that data is available and useable for analysis, reporting, and other applications by automating the processes of ingesting, processing, and storing it from several sources. To build these pipelines, data engineers frequently utilize Python programming languages or ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) solutions.Scalability and Performance Optimization: Ensuring that data systems can effectively handle massive volumes of data is the responsibility of data engineers. To achieve scalability and high performance, this entails fine-tuning database setups, refining data processing methods, and utilizing distributed computing frameworks such as Apache Hadoop or Apache Spark. Data engineers also keep an eye on system performance and adapt as necessary to maintain optimal throughput and response times.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
Ensuring that data systems can effectively handle massive volumes of data is the responsibility of data engineers. To achieve scalability and high performance, this entails fine-tuning database setups, refining data processing methods, and utilizing distributed computing frameworks such as Apache Hadoop or Apache Spark. Data engineers also keep an eye on system performance and tweak as necessary to keep throughput and response times at their best.
Free CDNData Quality Management
Accurate and trustworthy insights must be produced, and maintaining data quality is essential. Data engineers employ procedures and instruments, such as anomaly detection, data cleansing methods, and data validation tests, to monitor and enhance data quality. Data engineers contribute to ensuring the reliability and consistency of the data used for analysis and decision-making by creating governance frameworks and standards for data quality.
Data Engineering
What is data engineering?
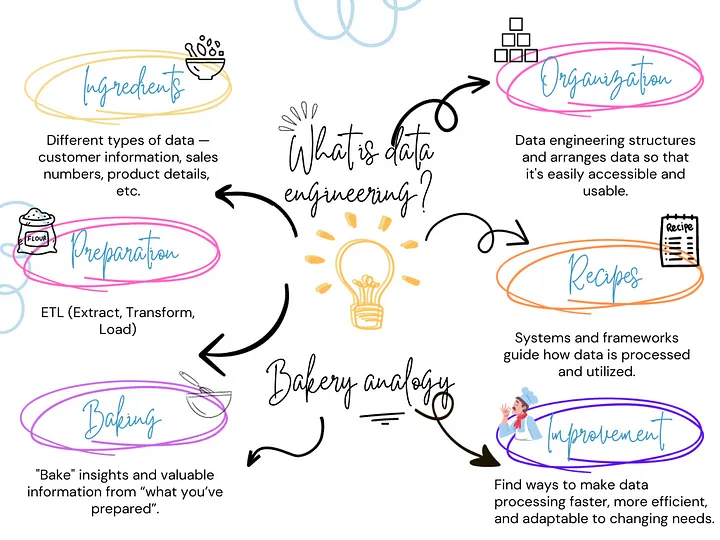
The process of gathering, organizing, and processing data in order to make it meaningful, accessible, and used is known as data engineering. To put it simply, data engineering is the process of building a strong foundation for data in order to maximize its potential for generating insights and advancing organizational objectives.<br><br>
Now let’s describe data engineering with a straightforward analogy.<br><br>
Assume you own a bakery, and one of your employees is in charge of making sure that all the components required to make mouthwatering pastries are on hand, arranged neatly, and prepared for use. Data engineering can be compared to the role of master organizer and facilitator in a bakery.
Benefits
Increased Data Accuracy
Data engineering makes sure that the data is consistent and of high quality, which results in more trustworthy conclusions and well-informed choices.
Performance and Scalability
High performance and scalability are maintained while managing massive data volumes through the use of effective data processing pipelines.
Cost Reduction
Cloud-based solutions and improved data workflows cut down on operating and infrastructure expenses.
Faster Time-to-Insight
Agile decision-making and faster insights are made possible by streamlined data pipelines, which facilitate faster data processing.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Teams can concentrate on higher-value work and innovation when manual labor is reduced by automated data operations.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations can innovate, remain ahead of the competition, and adjust to shifting market demands by utilizing data successfully.




